Do you know where drinking water comes from?
In South Florida, drinking water comes from Everglades, a wide range of wetlands, which lived in millions of people.
However, the ever-centers shrink in the last century, the water supply and water quality has become a threat, including the fuel of the flow of agricultural flow. Now the water supply faces another rising challenge: salty water intervention.
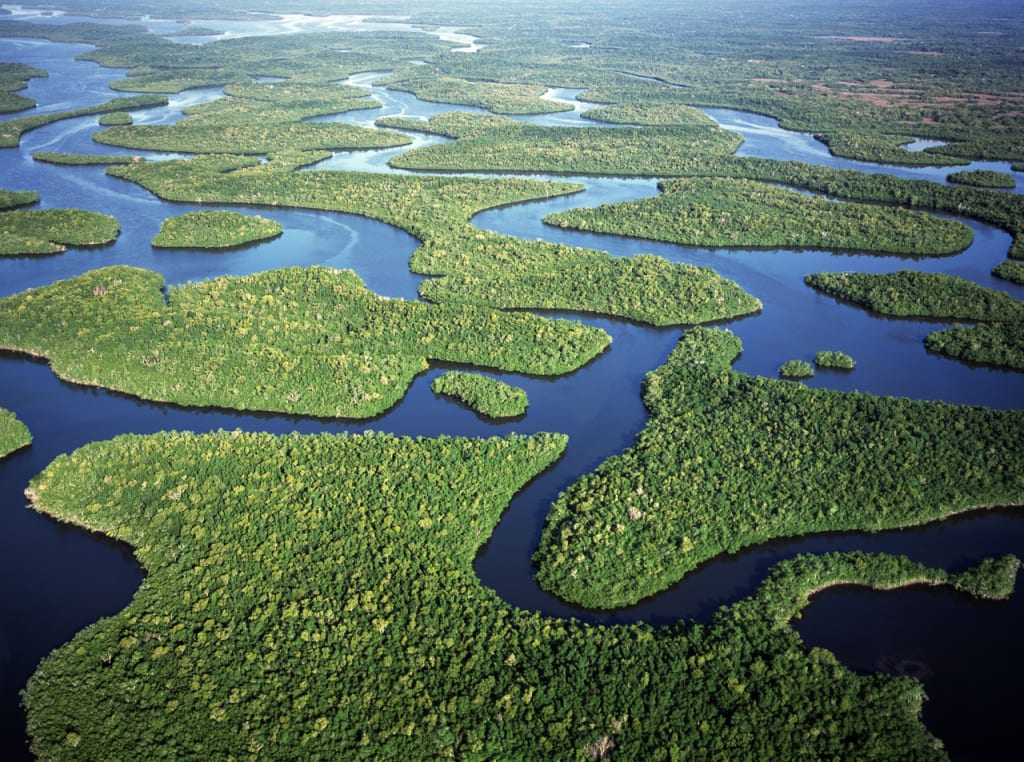

To protect water hinges to restore the evergreens of South Florida. Therefore, 25 years ago, the federal government and universities began to restore the world’s largest ecosystem.
I am participating in this work ecosystem as an ecologist. The risks I continue to restore Everglades today are more important than ever.
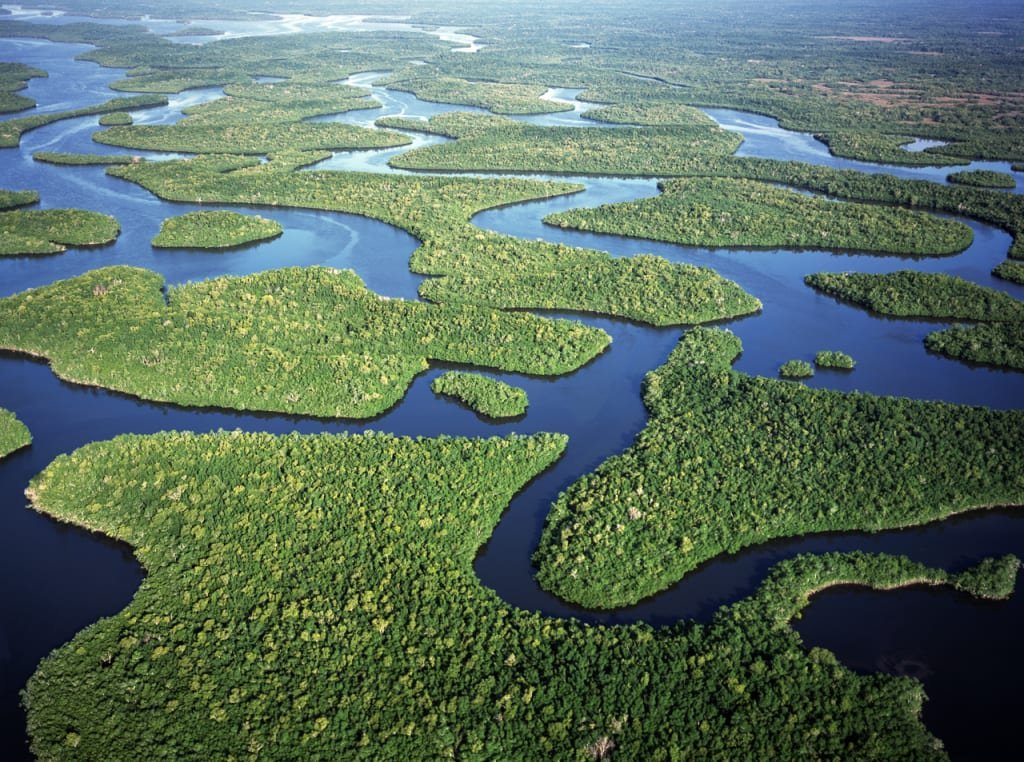
What happened in Everglades?
Florida Everglades, sweet juice, sawfalls, cych dome and wooden islands, mangrove forests and seashores, broad mosaics with all water through the sea.
But it is half of its original size. In the early 1900s, the US Army Corps of Engineers and people began to install channels and leve to control the floods in Everglades, which allow them to build farms and communities. Tamayami Trail became the first way between Everglades in 1928. This was connected by Tampa to Miam, but the roads and channels cut or expelled some natural water flow of South Florida.
Since then, Florida’s economy, agriculture and the population exploded and had a food problem in Everglades with them.
Everglades grows in a swollen area south of Oceanechobee Lake, which covers 1100 square miles known as the agricultural sector. About 80 tons of phosphorus fertilizers from federal subsidized farmlands, each year Everglades flows in wetlands. And it turned into the quality of water. High nitrogenous water drinking water is associated with human health problems, and phosphorus and related algal flourishing can lead to toxins such as mercury of germs.
Healthy wetlands can filter these foods and other pollutants that clean the water.
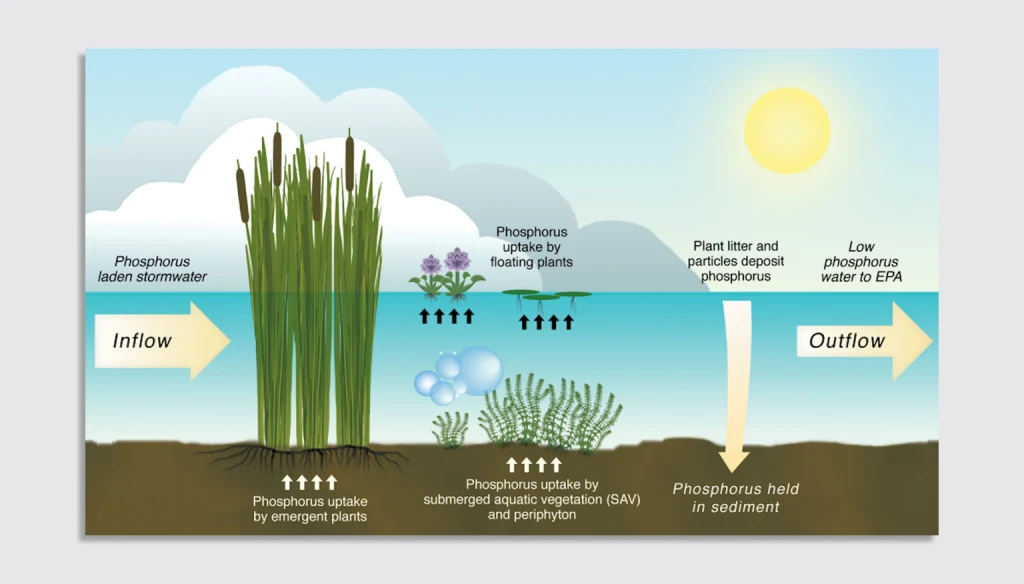
Raining rain in Everglades is staff with a porous limestone, and 1 in 3 floridians fills the Biscayne Suifer, drinking drinking water.
However, the wetlands need time and place to work properly and harmed the natural filtering system damage from farm pollution.
In the 1990s, Everglades hit a wild stress level in wetlands and wildlife in the wildlife, and burning the farms of farms and burning the growth of innovative species.
Changes caused Seagrass’s death and caused a wide range of saw swamps by Cattail and Harmful Algal Blooms. The collapsed wetlands can contain sources of contamination with pollution sources that can reduce oxygen and groundwater quality in water that can damage it in water.
A wide restoration campaign
The Congress approved a comprehensive Everglades recovery plan to reduce the deeper water depth and reducing the deepest depth of natural water in 2000 and reduced more natural water depth.
These recovery efforts are reworked to the flow of wetlands, reworking the flow of natural water, progress in the recovery of large areas. Phosphorus levels are lower in many moisturized wetlands and helps provide sweet water with drinking water supply in this wetland.
However, the delays of critical significant components of this work have left the places in the nearest and in the nearest and lower part of the agricultural area, especially in particular, especially the phosphorus concentration.
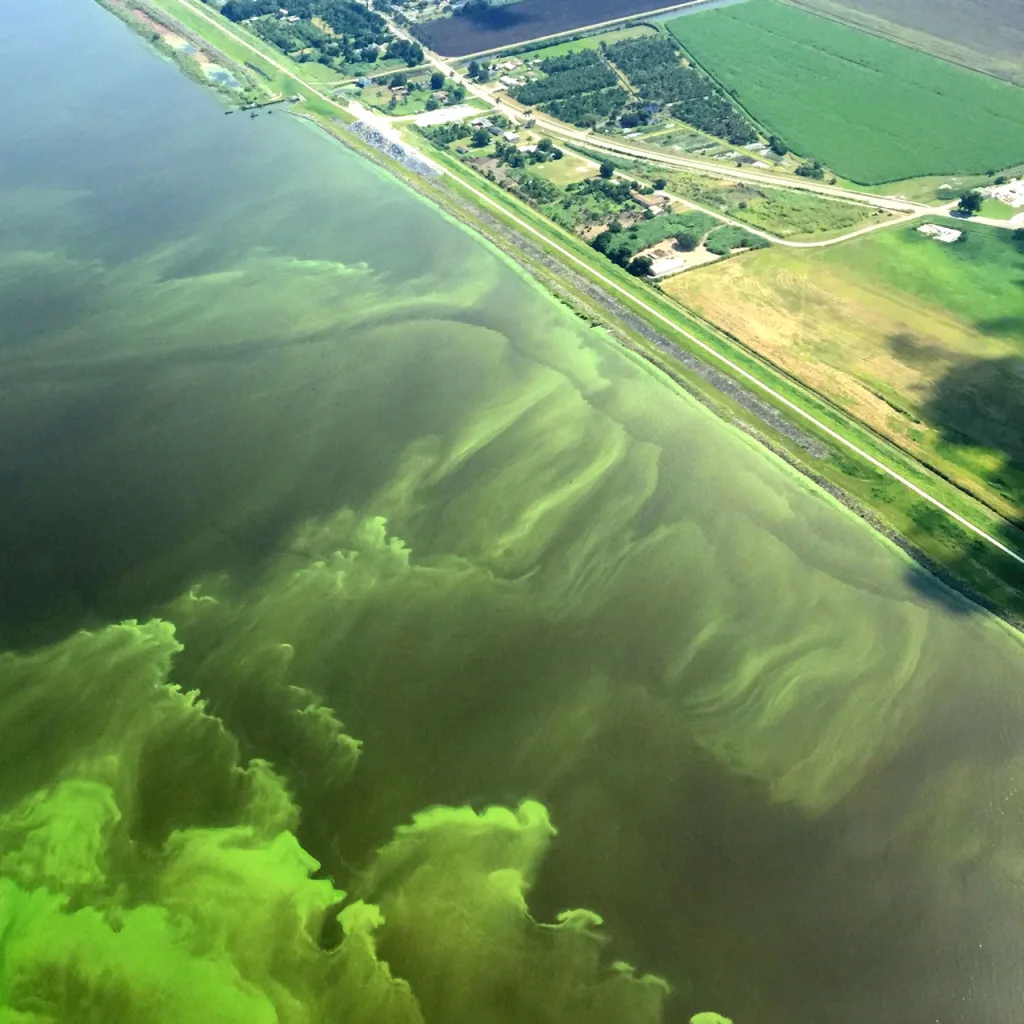

South Florida continues to prosper the harmful algal, which reaches the phosphorus and coast, as a result, killing fish and resulting in the death of manats. The red tide closes fishing and removes tourists going to the beach, hurts the local economy. The cost of this pollution in 2018 is estimated to be $ 2.7 billion in the cost of the Florida economy.
Unexpected Risk: Salty Water
An infected threat began to creep into the Everglade: salty water.
When the sea level rises, saline water, both rivers and underground, underground limestone through the aerated limestone under the South Florida. Although there is also a low water hits to drink subwares or watering water, the intervention of saline water is also occurring. Salt juice causes parts of the swamps of Everglades, often called the grass river, crashes into open water.
The loss of these freshwater swamps reduces the power of Everglades to remove the water phosphorus. And it means more nutrients that cause more food, water to pollute water, water folds and cause harmful algal flourishing.
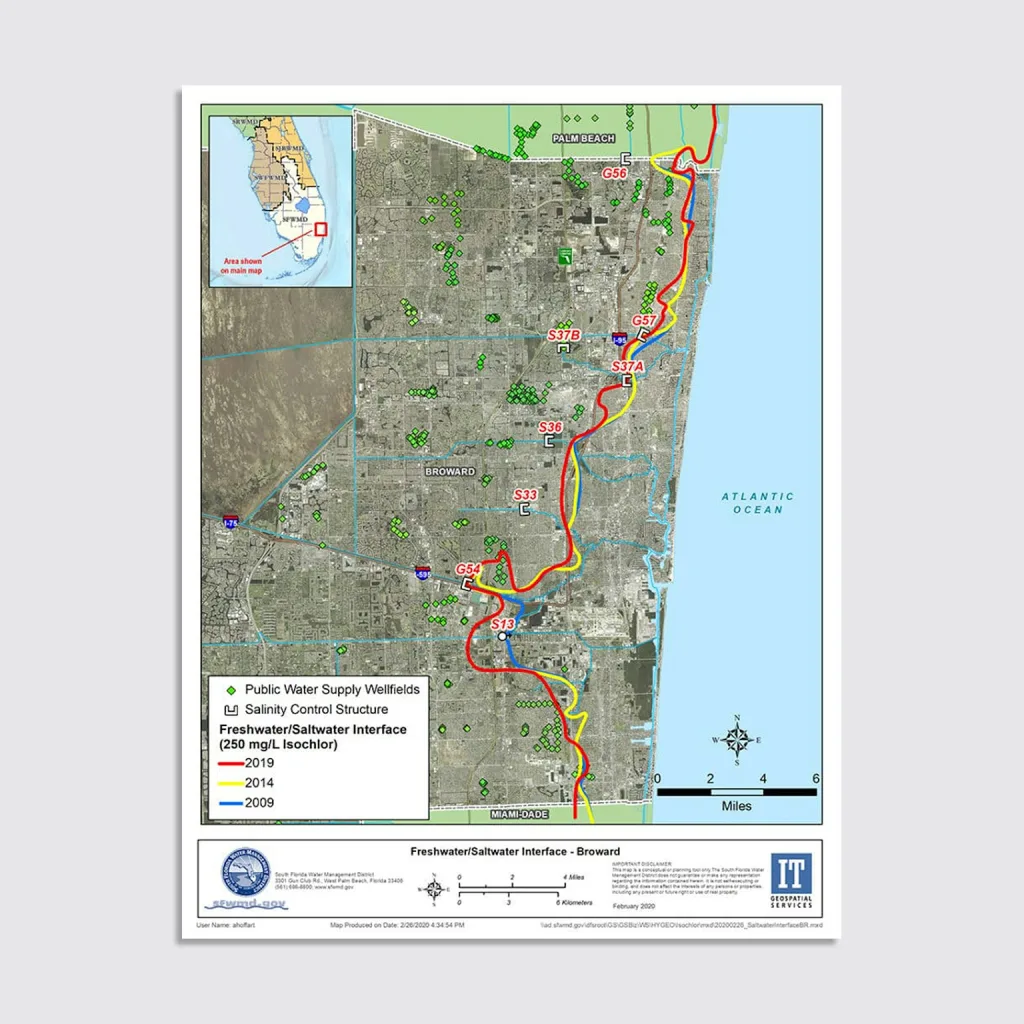
Scientists needed fresh water pause, sweet water beans in the shock season, sweet water beans, to escape the intrusion of salty water.
For example, saline juice intervated a mile in the areas of the region of Fort Lauderdale region between 2009 and 2019. Salt waters need more fresh juice to push back to the sea.
However, the recovery efforts were never intention to fight salt water intervention.
Causes of optimism
Despite sustainable problems, I am optimistic about how scientists, politicians and communities work to protect their evergreen and drinking water.
Florida Coastal Everglades I take part of this restoration work through the long-term environmental research program. The effort that started at 1 May 2000 at the International University of Florida was approved by the Everglades Recovery Plan Congress.
We were used to determine the level of nutrients for our research to protect the water supply of the region and worked for South Florida for 25 years to provide drinking water to drinking water and clean water. We use our continued investigations to inform water managers and politicians of the best practices to reduce salt water and pollution.
As the mother of salt water continues to threaten South Florida, Everglades restoration and protection will be increasingly important.
Anyone in the region can help.
With the restoration of freshwater areas, South Florida, which allows you to reduce the use of freshwater in the meadows and plants, which allows you to reduce the use of freshwater in the Everglades ecosystems, can keep drinking water safe for the generations of future residents and visitors. This is something everyone can contribute.
Marjory Stoneman Douglas, Miami’s popular conservation, which helps Miami to build a national park, “Everglades is a test. If we pass, we can save the planet.”
John Kominoski is a professor of Biological Xcians at the International University of Florida.
This article was re-published from the conversation under a creative commons license. Read the original article.
